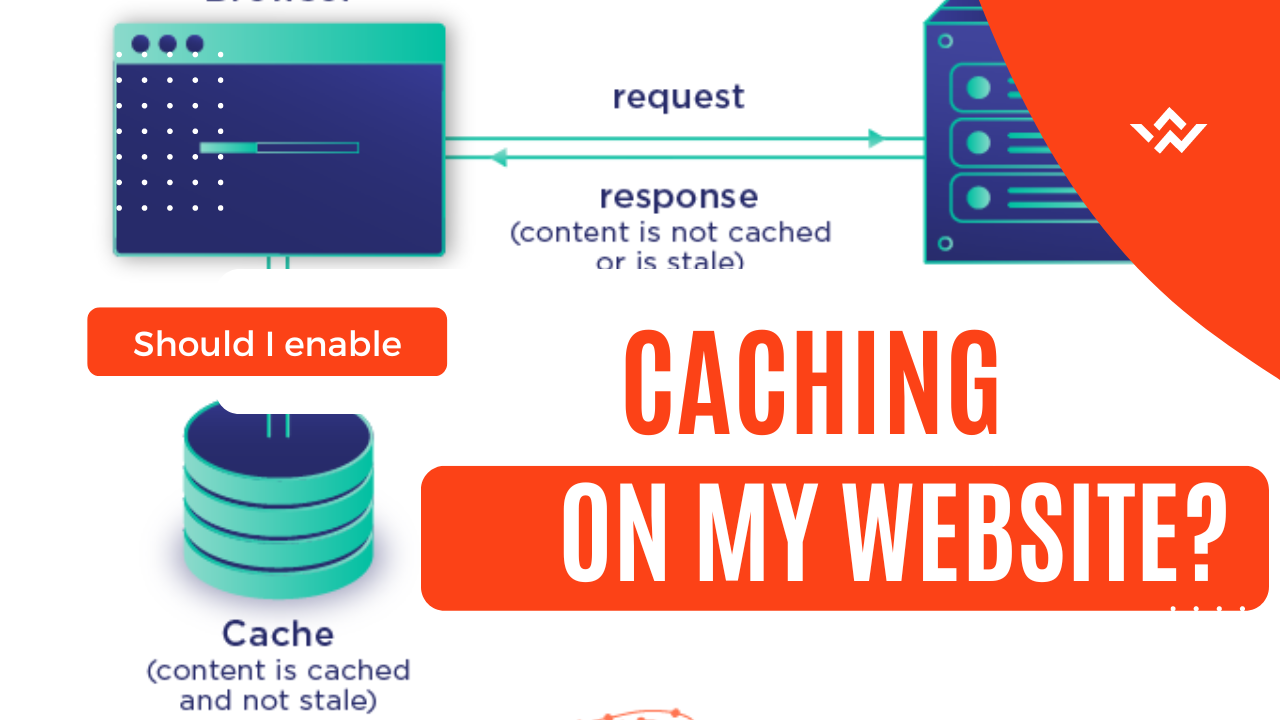
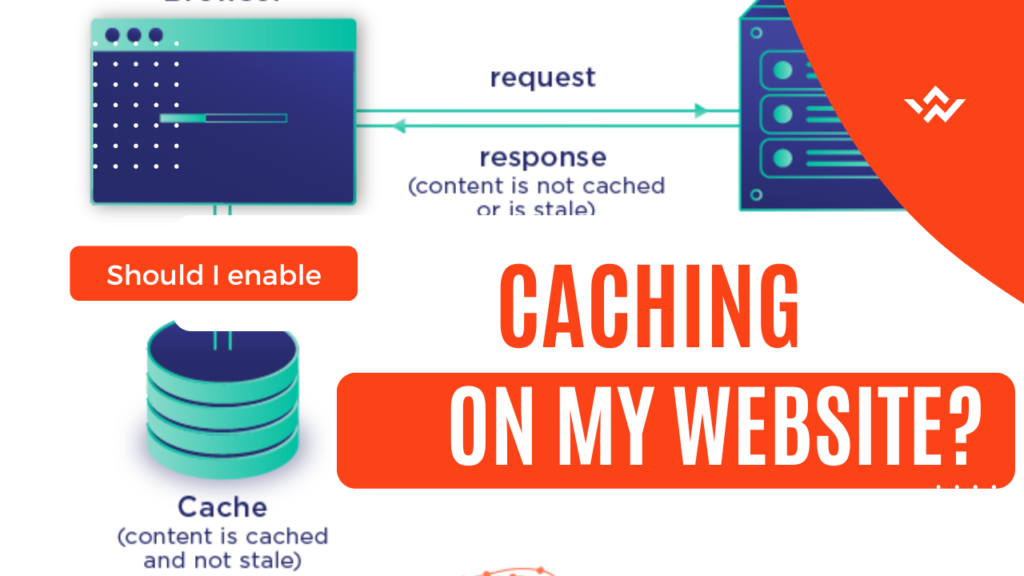
Caching is one of the main reasons why pages take so long to load. A visitor’s browser must send numerous separate requests for resources like photos, CSS files, and JavaScript files if caching is not enabled. In addition to slowing down your website, this consumes energy and increases your website’s emissions.
Contents
What is website caching and why is it so important?
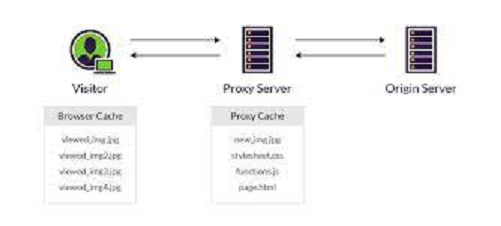
Simply defined, caching makes a copy of the website that has been requested and provides it to the user’s browser, which speeds up website performance and minimizes load times. Web caching functions by keeping the site’s data in a location that is physically closer to the visitor.
Why enable caching on a website?
Yes, you should enable caching on your website. Caching has many advantages, one of which is that it can enhance site performance. As we mentioned, That’s because your content will load considerably more quickly if you enable caching. Browsers can simply view your website without repeatedly requesting its files by keeping files locally. That will improve your users’ experience which will affect your SEO performance directly of course. You may like to read this article about caching best practices.
How does website caching work?
Let’s examine the procedures a visitor goes through when visiting your website in order to comprehend the process of website caching:
- Your visitor types your website’s address into the browser
- The browser then makes an HTTP request to your web server to get the necessary page content.
- The HTTP request is received by your web server, which subsequently processes it.
- Your website’s server downloads the necessary files in HTML format and sends them to the visitor’s computer.
- Finally, the transferred data are received by the visitor’s browser, which then processes them to display the website.
Every time a visitor accesses the same web page, these five stages are repeated. As your web server must process each HTTP request, this procedure takes time and uses resources.
So, The benefits of caching include speed, efficiency, and the reduction of server load as a result of caching.
How long should pages be cached?
We advise caching static assets or materials that don’t change often, for at least one week and ideally for up to one year. We advise utilizing a URL fingerprinting or versioning strategy if you need fine control over when resources are invalidated.
When should you stop caching?
The main drawback of caching is that a client can be viewing outdated information since your website, not the server or the browser, may have been cached. The browser won’t be able to check the cached content and the website may load out-of-date content if the cache strategy is not properly specified and configured, which can have a negative effect on the user experience. It’s crucial to comprehend how both the server cache and the browser cache work, especially if your website frequently distributes time-sensitive material, like online stores. These problems may be found in both of these caches.
Is website caching good for SEO?
Additionally, statistics suggest that 40% of users will leave your website if it takes longer than three seconds for your content to load. Consequently, you may simply lower your bounce rates when you use caching. You can make your visitors’ experience less annoying by doing this.
Caching the files on your website might also help with SEO. That’s because Google takes page speed into account when evaluating your website and uses it to determine search rankings. This implies that keyword targeting and other SEO strategies, such as caching, may be equally crucial.
Despite the fact that caching can make your website faster for subsequent visitors, your browser will still execute initial HTTP requests. Consider additional factors that contribute to a slow page speed in addition to caching, and work on optimizing your content.

Conclusion
Caching makes browsing better and faster. Cookies stay (for a while) on your computer once it has been downloaded. Regardless of how fast your Internet connection is, getting files from your hard drive always takes less time than retrieving them from an online server.